Sales forecasting
and inventory optimization
Become a retail mastermind you always wanted to be.
Become a retail mastermind you always wanted to be.
By: Jul Domingo
The retail industry already knows it: Better inventory management = faster growth.
But inventory management is a complex matter, involving different steps from the minute you order from your supplier to the moment the product makes its way into your customers’ hands.
The simplest hack to improve it is to monitor your inventory performance.
And as with all things related to performance, defining key performance indicators (KPIs) is a good place to start. You can use them as your compass to determine how close you are to achieving your goals.
In this piece, you’ll learn all things related to inventory management KPIs: how to choose them, what are the best ones to track, and why they matter.
There’s no strict rule in choosing the right inventory management KPIs. However, they must be as SMART—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and timely—as possible. Follow these suggested tips when deciding the best inventory KPIs for your organization.
If KPIs are the compass, strategic goals are the destination. For this reason, tailoring metrics to your goals is crucial to reaching tangible results.
First, identify the short-term goals you hope to achieve in the succeeding month or quarter. Do you intend to increase your sales? Set a specific and attainable target amount for each season.
For long-term goals, the following question can serve as your North Star: What do you expect to gain in the next three to five years?
As your business changes, ensure both short-term and long-term goals remain relevant.
Vanity metrics include feel-good numbers that don’t contribute to attaining your goals. Positive KPI results alone don’t indicate that you’re on the right course. Stick with actual performance metrics instead of vanity metrics to avoid getting sidetracked.
Consider this: a 100% service level rate (i.e., order delivered divided by order received) is a dream, right?
You never run out of stock, so you take it as a good sign. This could also be due to undetected bloated inventory, which may negatively impact your bottom line. There’s nothing wrong with measuring your service level, but you should include other KPIs like carrying cost and turnover.
These inventory management KPIs are better at showing you a realistic overview of what’s going on in your inventory.
Diagnosing your current performance is a practical way to determine your KPIs. Perform this step by observing your operations first-hand.
Is your team dealing with ineffective controls and processes? Ask for their input and determine the key persons involved.
For instance, you can cascade your KPIs down to the individual level instead of calculating averages over teams. This will hold them more accountable and help the right person take the necessary actions.
KPI overload can send your organization downhill rather than uphill. Imagine tracking over 100 inventory KPIs—do you have the time and patience to review them?
Even if you do, it’s still counterproductive and hardly sustainable in the long run.
Go back to your strategic goals, and select your current top three priorities from that list. After that, come up with at least three inventory management KPIs for each. The more you limit your KPIs, the more specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and timely they are.
Changes in your organization or team objectives are inevitable. That’s why reviewing your KPI results, perhaps with a scorecard or a dashboard, is crucial to the process.
Are your current measures still appropriate for the goals months or years later? If not, consider replacing or retiring the outdated ones.
As your business grows, your inventory KPIs may no longer be as relevant as they once were. So it’s always a good idea to update your key inventory metrics to reflect your new goals.
One of the most critical aspects of managing inventory is getting your predictions right. Inaccurate forecasts result in unsatisfied customers, lower sales, and higher holding costs.
Therefore, we consider demand forecast accuracy the most important KPI for inventory management. Many of your business decisions are based on how well you predict the future demand for your products.
This KPI measures how well your forecast aligns with your actual scales. Is there a huge disparity? When the anticipated demand closely matches what was sold–It’s a good sign you’re able to forecast demand well.
Measuring accuracy can be done in many ways. The two most common of which are:
If there’s a huge margin of error, best to address this head-on and start fine-tuning your forecasting processes or opting for a better software tool for better accuracy. More accurate forecasts are key to improving inventory purchasing and planning.
Check out this article for more information on inventory forecasting.
While customer satisfaction involves more than inventory, it accounts for a significant part of the overall picture.
Stock-outs have led to 39% of shoppers walking out of stores. While you can still score some of these potential sales, since surveyed millennials (75%) and Gen X (53%) shoppers left stores without purchasing, only to buy from the store’s website later.
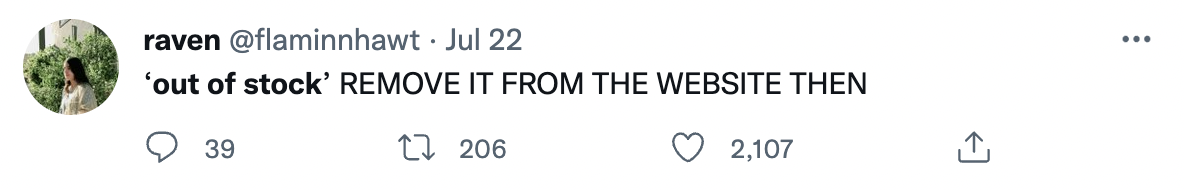
But if it’s not available there as well, they will happily complain on social media:
Source: Twitter
Expect these customers to look for alternative products–. Aside from compromising customer satisfaction, your bottom line can also suffer. Stockouts were shown to cause the retail industry a whopping $1 trillion in sales.
Another inventory-related factor you can do to enhance customer satisfaction is to offer various products–especially since 88% of Google survey respondents claimed that product selection and variety matter when picking a retailer. This is why we encourage our customers to keep a healthy product portfolio.
There are many ways to compute customer satisfaction: Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Effort Score (CES), and Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT score)–to name a few. But the easiest way is to perform a survey. It will give you more than figures, but also useful and actionable insights from your customers.
Maintaining consistent product availability and offering a sufficient selection makes shopping with you more enjoyable for your customers, resulting in repeat sales and long-term relationships. Use this inventory management KPI to pick products that will keep your customers returning.
The cost of carrying and holding inventory is important to examine but often goes unnoticed. However, leveraging it as an inventory management KPI will help you understand how unsold inventory affects your bottom line.
Excess holding costs can have a significant impact on profitability. In most industries, holding costs, are between 20% and 30% of total inventory value. It becomes more expensive the longer you keep an item.
Computing inventory carrying costs is complex because there are many factors to consider. But considering these expenses can business owners an idea:
High inventory turnover will help keep these expenses low. Avoiding overstocking and removing your slow-movers and dead stock help improve your profits. (Read these articles about overstocking and dead stock to find out how.)
Inventory turnover is an important yardstick for overall company efficiency.
It shows how often a company sells and replaces inventories, and the resulting information can be used to decide purchasing points, production, and even strategies surrounding marketing and pricing strategies.
Calculating inventory turnover involves two methods:
A fast inventory turnover can mean two things: fantastic sales or inadequate stock. We often see this in fast fashion retail brands (Zara and Shein) and department stores (Target and Walmart).
But a slow rate generally indicates weaker profits due to poor sales and increased holding costs from excess inventory. We say “generally,” since specialty/luxury items have low turnover, but remain profitable.
Given this fact, setting a standard inventory turnover rate is hard. The nature of your business will dictate your baseline. Although in most cases, companies will strive to maintain a high inventory turnover. Stock turnover reduces the amount of capital they have invested in inventory, improving cash flow.
The Sell-through rate represents how many units have been sold compared to the total inventory the supplier shipped. This inventory management KPI measures the efficiency of your supply chain and improves your replenishment practices.
A sell-through rate can determine which items are successful and which are pulling you back, especially in brick-and-mortar stores when sales are not increasing despite increased foot traffic. With this method, you can optimize displays to feature the products that sell the fastest and discard the ones that don’t.
Calculate your sell-through rate by dividing units sold by starting inventory during the period you want to analyze. Multiply the result by 100.
The sell-through rate gives a comprehensive picture of a business and a detailed analysis of how each specific product performs. A higher percentage indicates success.
Inventory accuracy measures how well warehouse stock records match actual stock levels.
A single error can lead to a whole host of problems, especially for ecommerce businesses. If your records show ample stocks online when you don’t have enough, shoppers will continue to buy the item. As a result, you’ll have to rush to acquire enough stock to satisfy customers waiting to receive their package.
But before using inventory accuracy rate as a KPI, ensure that the inventory records reflect reliable figures. Human errors are the common problem here, so you might want to consider using technology like barcode scanning software.
Calculating inventory accuracy is as simple as counting the number of items in stock that are currently available, dividing by the stock count on record, and multiplying the number by 100.
Leverage this inventory management KPI to reduce shortages, shrinkage, and stockouts.
Aging Inventory (Product) KPI refers to product inventory that has aged past its sell-by date and should be sold off.
This KPI helps answer questions about which products do not sell fast or require discounts for customers to take action.
Aging Inventory KPI requires the storage date of the inventory as well as the aging threshold in hours for the asset. It varies based on the product, especially for critical commodities with expiration dates, such as groceries.
Calculate aging inventory by dividing the cost of inventory by the cost of sold goods. Multiply this number by 365 to get the annual score. Older inventory, of course, costs more.
Learn more about inventory aging here.
It’s crucial to check your stock-to-sales ratio to see if you are running out of products. With this inventory management KPI, you can determine how much inventory you have kept on average over time.
A low ratio indicates that you don’t replenish your stocks as often as you should. You’re missing out on potential sales. Increasing your inventory will help you meet customer demands.
A high ratio, on the other hand, means you’re housing more goods than you should. Your warehouse costs are probably through the roof. Toning your purchases down can help keep your profits up.
Both, however, indicate you need to get better at forecasting. This circles back to our first one on the list: improving forecast demand accuracy.
Divide the average inventory value by the net sales achieved over a certain time period to calculate the stock-to-sales ratio. Multiplying this by 100 will give you the percentage.
It can take some time–years, not months–to monitor. Insights can help you optimize stock levels, boost profitability, and enhance sales strategies.
Setting goals is a wild-goose chase unless you track your progress. So whether that goal is to cut costs or reduce losses due to shrinkage, you must consider evaluating your performance.
Your inventory management KPIs are a reference for assessing your controls and processes against your strategic objectives. By knowing and tracking the right metrics, you’ll be able to:
Setting inventory management KPIs in place can steer you in the right direction. And to help you hit–or even beat–them, forecast, segment, and replenish your products better by working with Inventoro. We can help you gain footing as you take steps toward better inventory management processes.
Become a retail mastermind you always wanted to be.